Bilateral Sciatica
Unlock the mystery of bilateral sciatica with our comprehensive guide. Learn about symptoms, causes and effective treatment options. Don’t let pain rule your life—get the facts and take control today! As someone passionate about sciatica health and eager to provide helpful suggestions, this article on bilateral sciatica manifests as pain, numbness, or tingling in both legs. Unlike its unilateral counterpart, which affects just one side, bilateral sciatica often signals a more serious underlying issue. Common causes include herniated disks, spinal stenosis, and spondylolisthesis. This article provides valuable insights for understanding, diagnosing, and effectively managing this challenging condition.
What Is Sciatica
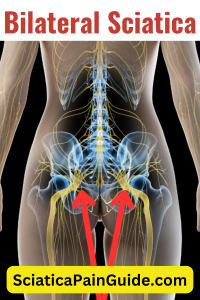
Sciatica refers to pain that radiates along the path of the sciatic nerve, which branches from the lower back through the hips and buttocks and down each leg. Typically, the condition affects only one side of the body and often results from a herniated disk, bone spur, or spinal stenosis.
Sciatica Or Hamstring Pain
Hamstring pain is generally muscle-related, and you can learn more here – how to tell the difference between sciatica and hamstring pain.
What Is Bilateral Sciatica?
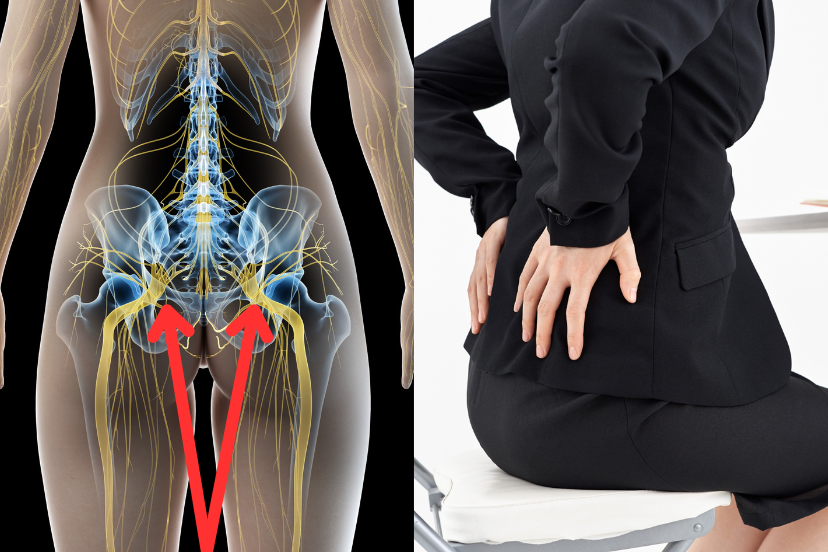
Bilateral sciatica causes pain, numbness, or tingling in both legs, affecting the path of the sciatic nerves on both sides of the body. Unlike typical sciatica, which usually impacts just one side, bilateral sciatica often indicates a more severe underlying issue. Common causes include herniated disks, spinal stenosis, or spondylolisthesis. Prompt medical evaluation and treatment are crucial for effective symptom management.
How Rare Is Bilateral Sciatica?
Bilateral sciatica is relatively rare compared to its unilateral counterpart, which more commonly affects just one side of the body. While precise statistics on its prevalence are hard to pinpoint, medical professionals generally agree that cases requiring treatment for bilateral symptoms constitute a smaller subset of overall sciatica incidents. Bilateral sciatica’s rarity often serves as a red flag for clinicians, prompting them to investigate more serious underlying conditions like severe herniated disks or spinal stenosis. Therefore, encountering bilateral sciatica requires a thorough medical evaluation and targeted treatment to address the root cause.
Why Is Bilateral Sciatica A Red Flag?
Bilateral sciatica is a red flag for medical professionals primarily because it is less common and often indicates a more serious underlying spinal condition. While unilateral sciatica usually affects one side and can result from less severe issues, the bilateral form suggests that significant spinal structures are involved. Causes like severe herniated disks, spinal stenosis, or spondylolisthesis commonly contribute to bilateral symptoms. Because these conditions can lead to more serious complications like chronic pain or muscle weakness, clinicians treat the presence of bilateral sciatica as a signal for an immediate, comprehensive evaluation and targeted treatment.
How To Relieve Sciatica Pain In Both Legs
Causes Of Bilateral Sciatica
There are several potential causes of bilateral sciatica. These include:
Herniated Discs
Herniated discs occur when the soft cushion between your spinal bones ruptures, causing the inner material to leak and irritate nearby nerves. This can happen on either or both sides of your lower back.
Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
This condition occurs when the spinal canal narrows, putting pressure on the nerves. If it affects both sides of the spine, it could cause bilateral sciatica.
Spondylolisthesis
In this condition, a lower vertebra slips forward onto the bone directly beneath it, which can press on the nerve and trigger symptoms in both legs.
Symptoms Of Bilateral Sciatica
The symptoms include pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness in both legs and the lower back. These symptoms can vary from mild to severe, and they can even affect mobility.
Bilateral sciatica refers to sciatic pain affecting both sides of the body. The symptoms are similar to regular sciatica but are experienced in both legs instead of just one. These may include:
Pain: It often starts in the lower back or buttocks and travels down both legs. The pain can range from a mild ache to a sharp, burning sensation or excruciating discomfort.
Numbness or Tingling: These sensations can be experienced in both legs or feet.
Weakness: You may have difficulty moving both legs or experience a loss of strength.
Changes in Bowel or Bladder Function: Although rare, these can indicate a serious condition called cauda equina syndrome, which requires immediate medical attention.
Is It Normal To Have Sciatica On Both Sides?
Having sciatica on both sides, known as bilateral sciatica, is less common than experiencing it on just one side, which is referred to as unilateral sciatica. While not “normal,” bilateral sciatica often raises concern among healthcare providers because it usually indicates a more severe underlying issue affecting the spine. Common causes include severe herniated disks, spinal stenosis, and spondylolisthesis. Because bilateral sciatica is generally less typical and often linked to more serious conditions, seeking medical evaluation is crucial. Early diagnosis and targeted treatment are essential for effective management and to prevent complications.
Is Bilateral Sciatica Dangerous?
Bilateral sciatica is not inherently dangerous, but it often indicates a more serious underlying spinal issue that requires prompt medical attention. Unlike unilateral sciatica, which generally affects just one side, bilateral symptoms suggest conditions like severe herniated disks, spinal stenosis, or spondylolisthesis may be present. In extreme cases, these underlying conditions can lead to more significant problems if left untreated, such as chronic pain, muscle weakness, or even loss of bowel or bladder control. Therefore, immediate evaluation and treatment are essential for managing bilateral sciatica effectively and preventing complications.
Complications Of Ignoring Bilateral Sciatica
Left untreated, sciatica on both sides of the body can lead to long-term nerve damage, loss of feeling in the affected limbs, and reduced function. Hence, it’s crucial to seek medical attention if you experience symptoms.
Diagnosing Your Pain
Diagnosing bilateral sciatica typically involves a multi-step process. Initially, healthcare providers conduct a thorough physical examination, which may include tests for muscle strength, reflexes, and pain distribution. Next, they usually order imaging tests like X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans to view the spinal structures in detail.
Physical Examination
Your doctor will ask about your symptoms and conduct a physical examination. This may involve checking your muscle strength and reflexes.
Imaging Tests
These may include MRI or CT scans, which can provide detailed spine images and help identify any issues causing your symptoms.
Your Treatment Options
Treatment options for bilateral sciatica include conservative methods and surgical options.
Conservative Methods
These involve physiotherapy, pain medication, and lifestyle modifications. Many people find relief from these non-surgical methods.
Surgical Options
If conservative methods aren’t effective, surgery might be recommended. This can include procedures like laminectomy or discectomy.
How To Prevent The Pain
To prevent bilateral sciatica pain, adopt a proactive approach that targets potential underlying causes. First, maintain good posture while sitting and standing to reduce stress on the spine. Incorporate regular exercise, focusing on core strengthening and flexibility, to support your back and minimize nerve compression. Manage your weight through a balanced diet, as excessive weight can exacerbate spinal issues. Avoid heavy lifting or, if you must lift, use proper techniques that engage your legs and core, not your back. Also, consider ergonomic furniture and supportive footwear to reduce spinal strain. Frequent breaks and movement during long sitting periods can also help. Consult a healthcare provider for a tailored treatment plan for persistent or recurrent symptoms.
What Is The Treatment For Bilateral Sciatica
Treatment for bilateral sciatica aims to address the root cause, alleviate pain, and restore normal function. Doctors often recommend conservative treatments like anti-inflammatory medications, physical therapy, and rest. Physical therapists design targeted exercises to strengthen the back and core, improving spinal health. If traditional measures fail, more aggressive options such as corticosteroid injections may be considered for temporary relief. Surgical interventions like laminectomy or microdiscectomy could be necessary in severe cases where spinal compression risks nerve damage. Alongside these treatments, doctors may also prescribe medications for pain management, including non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or muscle relaxants. Importantly, each treatment plan is individualized, considering the patient’s overall health, severity of symptoms, and underlying cause.
Tips For Living With Sciatica On Both Sides Of The Body

Maintaining A Healthy Weight
A healthy weight reduces pressure on your spine, which can alleviate sciatica symptoms.
Maintaining a healthy weight can help manage sciatica by reducing pressure on the spine and thus, the sciatic nerve. Extra weight, especially around the midsection, can alter spinal alignment and posture, exacerbating sciatica symptoms. A healthy diet and regular exercise help in weight management and promote overall spine health and well-being.
Regular Exercise
Exercises that strengthen your back and core can help manage and prevent sciatica.
Regular exercise helps manage sciatica by strengthening the muscles that support your spine, reducing pressure on the sciatic nerve. It also improves flexibility and posture, further alleviating symptoms. Exercise enhances blood circulation, promoting healing, and it triggers endorphin release, which can act as a natural painkiller. Regular, appropriate activity can prevent future sciatic flare-ups.
Proper Posture
Maintaining good posture, especially when sitting for long periods, can help prevent sciatica.
Proper posture can help manage sciatica by reducing pressure on the spine and the sciatic nerve. Good posture, whether sitting, standing, or moving, ensures even body weight distribution, preventing undue strain on the lower back. It promotes spine alignment, reduces muscle tension, and encourages healthier movement patterns, reducing the likelihood of sciatica flare-ups.
Using Ergonomic Furniture
Chairs and desks that support good posture can reduce the risk of sciatica.
Ergonomic furniture can help manage sciatica by promoting proper posture and evenly distributing body weight, reducing pressure on the spine and sciatic nerve. Ergonomic chairs and desks can provide appropriate support to your lower back and thighs, while adjustable features can help maintain optimal posture during prolonged sitting, reducing strain and discomfort associated with sciatica.
Is Bilateral Sciatica A Disability?
Bilateral sciatica itself is not automatically classified as a disability. However, its severity and impact on daily activities can sometimes meet the criteria for disability status, depending on jurisdiction and specific case assessments. If the condition significantly impairs your ability to perform work-related tasks or engage in normal daily activities for an extended period, you may qualify for disability benefits. Accurate diagnosis and documentation by healthcare providers are crucial in such instances. If you experience debilitating symptoms, consult medical professionals for a thorough evaluation and discuss options for work accommodations or disability benefits.
Is Bilateral Sciatica Curable
Whether bilateral sciatica is curable depends on the underlying cause. In many cases, conservative treatments like physical therapy, anti-inflammatory medications, and lifestyle changes can effectively manage symptoms and even resolve the condition. However, in instances where severe herniated disks, spinal stenosis, or other significant spinal issues are the root causes, surgical intervention might be necessary. Even with surgery, there’s no guarantee of complete symptom eradication. Some people may experience recurrent or chronic symptoms. It’s crucial to consult with healthcare providers for an accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plan. Early intervention often leads to better outcomes, but complete cure varies from case to case.
Last Stages Of Sciatica
In the last stages of sciatica, symptoms generally either resolve or become chronic, depending on the effectiveness of treatment and the underlying cause. Targeted treatments like physical therapy and medications lead to significant improvement or even complete relief for many. However, symptoms may persist despite treatment efforts if the condition becomes chronic. Long-term pain management strategies, including medications, lifestyle adjustments, and possibly surgical interventions, become essential in such cases. Constant medical monitoring is critical to adapt the treatment plan and prevent complications.
When To Seek Medical Help
Seek medical help for bilateral sciatica when you notice symptoms like pain, numbness, or tingling in both legs. Immediate consultation is especially crucial if the discomfort affects your ability to perform daily activities or work or if symptoms worsen rapidly. Additional red flags include severe pain, muscle weakness, and loss of bowel or bladder control, which could indicate a more serious spinal issue requiring urgent attention. Prompt diagnosis and treatment often lead to more effective management and better outcomes.
Bilateral Sciatica – Conclusion
Living with sciatica on both sides of the body involves managing symptoms through various strategies. Pain relief methods such as medications, hot/cold therapy, and massages can be used. Regular, gentle exercises and stretches under the guidance of a physical therapist can help improve strength, flexibility, and posture. Ergonomic furniture promotes better body alignment while sitting. Weight management and good sleeping positions can reduce pressure on the sciatic nerves. Lastly, medical treatments or surgeries may be options for severe cases.
Living with sciatica on both sides of the body can be challenging. However, understanding the condition, seeking proper treatment, and making lifestyle adjustments can significantly improve the quality of life.
Please note that this article should not replace professional medical advice. Consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plan.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Can bilateral sciatica be cured?
While it can’t always be completely cured, many people effectively manage and alleviate their symptoms with the proper treatment and lifestyle changes.
2. Is exercise safe for someone with bilateral sciatica?
Yes, but it should be done under a healthcare provider’s or physical therapist’s guidance to avoid worsening symptoms.
3. Can I prevent pain from both sides of the body?
Prevention isn’t always possible, but maintaining a healthy lifestyle can reduce your risk.
4. What type of surgery is used for bilateral sciatica?
It depends on the underlying cause. A discectomy or a laminectomy might be recommended.
5. Can I live a normal life with sciatica on both sides of the body?
Absolutely. People with bilateral sciatica can lead full, active lives with proper management.