Diagnosing Sciatica
Discover effective methods for diagnosing sciatica. Learn about treatment options, lifestyle modifications, and more. Get relief today! Sciatica is a common condition characterized by pain that radiates along the sciatic nerve, which extends from the lower back down through the buttocks and into each leg. As an enthusiast and advisor on sciatica, I understand the importance of accurate diagnosis in effectively managing this condition. In this article, I’ll provide insights into diagnosing sciatica, offering helpful suggestions and reasons for these suggestions.
Introduction to Sciatica
Sciatica occurs when the sciatic nerve becomes compressed or irritated, leading to pain, numbness, tingling, or weakness in the lower back, buttocks, and legs. It is often a result of underlying conditions such as a herniated disc, spinal stenosis, or muscle spasms.
Symptoms of Sciatica
Sciatica symptoms typically include pain that radiates along the path of the sciatic nerve, from the lower back down the buttocks and into the legs. The pain can vary from mild to severe and may be accompanied by numbness, tingling, or weakness in the affected leg. Symptoms may worsen with movement, prolonged sitting, or standing. Individuals may also experience difficulty walking or standing up. Sciatica symptoms can significantly impact daily activities and quality of life, necessitating proper diagnosis and management to alleviate discomfort and prevent complications.
Diagnosing Sciatica
Diagnosing sciatica involves a comprehensive evaluation, including medical history, physical examination, and possibly imaging tests or nerve studies. Proper diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment tailored to individual needs.
Self-Tests: Do You Have Sciatica?
Importance of Proper Diagnosis
Proper diagnosis of sciatica is essential for several reasons. It helps identify the underlying cause, such as a herniated disc or spinal stenosis, guiding appropriate treatment. Accurate diagnosis also rules out other potential conditions with similar symptoms, ensuring that individuals receive the most suitable interventions. Additionally, it allows healthcare providers to monitor the progression of the condition and adjust treatment strategies as needed, optimizing outcomes and improving quality of life.
Medical History and Physical Examination
A healthcare provider will take a detailed medical history and perform a physical examination during the initial evaluation. This helps assess the severity of symptoms, identify any red flags, and determine the appropriate course of action.
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests such as MRI, X-ray, or CT scan may be ordered to visualize the spine and identify any structural abnormalities, such as herniated discs or spinal stenosis. These tests provide valuable information about the location and extent of nerve compression.
Nerve Conduction Studies
Nerve conduction studies may be recommended to assess the function of the sciatic nerve and identify any areas of nerve damage or dysfunction. This test measures the speed and strength of electrical signals traveling along the nerve.
Differential Diagnosis
It’s essential to differentiate sciatica from other conditions that may present with similar symptoms, such as piriformis syndrome or sacroiliac joint dysfunction. Certain red flags, such as loss of bowel or bladder control or progressive weakness, may indicate a more serious underlying condition requiring immediate medical attention.
Role of Healthcare Professionals
Seeking guidance from a healthcare professional, such as a primary care physician or orthopedic specialist, is essential for the proper diagnosis and treatment of sciatica. They can offer expert advice, perform necessary tests, and recommend appropriate interventions based on individual needs.
Self-Assessment and Symptom Tracking
In addition to medical evaluation, self-assessment, and symptom tracking can provide valuable insights into the progression of sciatica symptoms. Keeping a pain journal to record the location, intensity, and duration of pain episodes can help identify patterns and triggers, informing treatment decisions.
Understanding Test Results
Understanding and interpreting test results is crucial for informed decision-making. Healthcare providers can explain the findings of imaging tests and nerve conduction studies, ensuring that patients clearly understand their condition and treatment options.
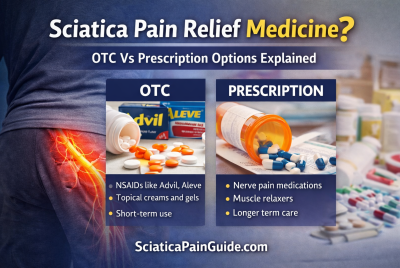
Treatment Options for Sciatica
Treatment options for sciatica vary depending on the severity and underlying cause of the condition. Conservative treatments include rest, physical therapy, and medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to alleviate pain and inflammation. Invasive procedures like epidural steroid injections or surgery may be considered for persistent or severe symptoms. Additionally, lifestyle modifications such as maintaining proper posture, regular exercise, and weight management can help reduce symptoms and prevent recurrence. Holistic approaches like acupuncture and chiropractic care may also provide relief for some individuals.
The Importance of Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in managing sciatica and preventing its recurrence. Maintaining proper posture, avoiding prolonged sitting or standing, and incorporating regular exercise can help alleviate pressure on the sciatic nerve and strengthen supporting muscles. Weight management reduces stress on the spine, while healthy dietary choices can reduce inflammation. Moreover, quitting smoking improves blood flow and promotes healing. Consistently practicing these modifications not only alleviates symptoms but also improves overall health and well-being, enhancing the effectiveness of other treatment modalities and reducing the likelihood of future flare-ups.
Prevention Strategies
Preventive measures such as maintaining a healthy weight, practicing good ergonomics, and avoiding activities that strain the back can help reduce the risk of developing sciatica or experiencing recurrent episodes.
Holistic Approaches
In addition to conventional treatments, holistic approaches such as acupuncture, chiropractic care, and mind-body techniques like yoga and meditation may offer relief from sciatica symptoms and improve overall well-being.
Support Networks and Resources
Joining online communities or support groups for individuals with sciatica can provide valuable emotional support, practical tips, and resources for managing the condition effectively.
The Role of Nutrition
Adopting an anti-inflammatory diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids may help reduce inflammation and promote nerve health. Certain supplements, such as vitamin B12, magnesium, and turmeric, may also have beneficial effects.
Long-Term Management
Managing chronic sciatica requires a comprehensive approach that addresses both physical and emotional aspects of the condition. Regular monitoring, lifestyle modifications, and ongoing communication with healthcare providers are key components of long-term management.
FAQs Related to Diagnosing Sciatica
Is sciatica a permanent condition?
Sciatica can vary in duration and severity. While some cases resolve with conservative treatments, others may become chronic. Proper management can alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life, but in some instances, sciatica may persist as a long-term or recurring condition.
Can sciatica be cured without surgery?
Yes, sciatica can often be managed effectively without surgery. Conservative treatments such as physical therapy, medication, and lifestyle modifications are typically the first line of defense. These approaches can alleviate symptoms and address the underlying causes, offering relief and improving the quality of life for many individuals with sciatica.
Are there any exercises that can worsen sciatica symptoms?
Yes, specific exercises or activities can exacerbate sciatica symptoms. Movements that involve heavy lifting, twisting, or bending at the waist may increase pressure on the sciatic nerve, leading to increased pain and discomfort. It’s essential to avoid or modify such exercises to prevent worsening of symptoms.
How long does it take to recover from a sciatica flare-up?
Recovery time from a sciatica flare-up varies depending on factors like the severity of symptoms and the effectiveness of treatment. While some individuals may experience improvement within days, others may require weeks for symptoms to resolve. Consistent management and adherence to treatment recommendations can expedite recovery.
When should I seek medical attention for sciatica?
Seek medical attention for sciatica if experiencing severe or worsening pain, weakness or numbness in the legs, or loss of bowel or bladder control. These symptoms may indicate a serious underlying condition requiring immediate attention. Early intervention can prevent complications and facilitate effective treatment.
Diagnosing Sciatica – Conclusion
In conclusion, diagnosing sciatica involves a thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional, including a medical history, physical examination, and possibly imaging tests or nerve studies. Proper diagnosis is essential for developing an effective treatment plan tailored to individual needs, which may include conservative measures, invasive procedures, lifestyle modifications, and holistic approaches. By understanding the importance of accurate diagnosis and exploring various treatment options, individuals can effectively manage sciatica and improve their quality of life.
Disclaimer
Please note that the information provided in this article is for informational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. If you’re experiencing sciatica pain or any health concerns, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.