Lesser Sciatic Notch And Its Impact On Sciatica
Discover the role of the lesser sciatic notch in sciatica and how it impacts managing and preventing sciatica pain. Dive in to find more! Learn how it serves as a crucial passageway for muscles and nerves, and explore conditions that could cause pain in this region. Unlock the mysteries of your body! As an advisor on sciatica, I want to shed light on an often overlooked aspect of this condition. Understanding the role of the lesser sciatic notch in sciatica can provide valuable insights into managing and preventing this debilitating condition. In this article, we will explore the lesser sciatic notch and its relationship with sciatica and offer practical suggestions on caring for it to alleviate symptoms and promote overall well-being.
What Is The Lesser Sciatic Notch?
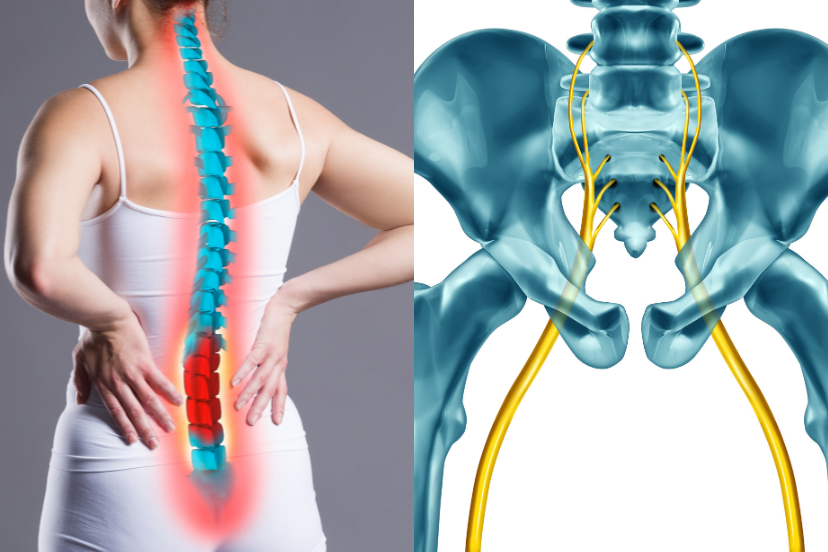
The lesser sciatic notch is a small, U-shaped depression in the pelvic bone, specifically in the ischium. It lies below the greater sciatic notch and separates the ischial spine from the ischial tuberosity. This notch serves as a passageway for several structures, including nerves and muscles. The obturator internus muscle, for instance, exits the pelvis through this notch, allowing it to attach to the femur. Various ligaments, such as the sacrospinous and sacrotuberous ligaments, also help convert the lesser sciatic notch into a foramen. In summary, the lesser sciatic notch plays a role in both skeletal anatomy and the passage of soft tissue structures.
Greater And Lesser Sciatic Notch
The greater and lesser sciatic notches are anatomical features found in the pelvic bone. The greater sciatic notch lies above the ischial spine and serves as a pathway for major structures like the sciatic nerve and piriformis muscle. The lesser sciatic notch sits below the ischial spine and is smaller in size. It acts as a passageway for the obturator internus muscle and specific nerves. Both notches transform into foramina when ligaments such as the sacrospinous and sacrotuberous ligaments attach to them. These notches play crucial roles in skeletal anatomy and the movement of soft tissue structures.
Structures Passing Through Greater And Lesser Sciatic Notch
What Is The Greater Sciatic Notch Used For?
The greater sciatic notch serves as an anatomical passageway in the pelvic bone, located above the ischial spine. It allows major structures, such as the sciatic nerve and piriformis muscle, to exit the pelvis and enter the posterior thigh. Various ligaments, including the sacrospinous and sacrotuberous ligaments, attach to the pelvic bone near this notch, converting it into a foramen. By providing this pathway, the greater sciatic notch plays a critical role in both motor and sensory functions of the lower extremities, as well as in overall skeletal anatomy.
Understanding Sciatica
Before delving deeper into the relationship with sciatica, it is essential to comprehend what sciatica entails. Sciatica refers to the pain, numbness, or tingling sensation that radiates along the path of the sciatic nerve, which extends from the lower back down to the legs. It is often caused by compression or irritation of the sciatic nerve.
What Is The Origin Of The Sciatic Nerve?
The sciatic nerve originates in the lower back, specifically from the lumbar and sacral regions of the spinal cord. It forms from the merging of nerve roots L4 to S3. These roots combine to create the largest nerve in the body. After its formation, the sciatic nerve descends through the pelvis and passes beneath the piriformis muscle. It then travels down the back of the leg, branching into smaller nerves that innervate the thighs, legs, and feet. The sciatic nerve plays a vital role in the lower extremities’ motor and sensory functions.
Definition Of Sciatica
Sciatica is a condition characterized by the inflammation or irritation of the sciatic nerve, resulting in pain and discomfort that can extend from the lower back to the buttocks and legs. The pain can vary in intensity and may be accompanied by other symptoms such as numbness and tingling.
Causes Of Sciatica
Sciatica can be caused by various factors, including herniated discs, spinal stenosis, muscle spasms, and even pregnancy. These conditions can lead to compression or irritation of the sciatic nerve, triggering the characteristic pain and discomfort.
Symptoms Of Sciatica
Common symptoms of sciatica include shooting pain along the sciatic nerve pathway, numbness or tingling in the buttocks or legs, muscle weakness, and difficulty in moving the affected leg or foot. The severity and frequency of symptoms can vary from person to person.
Lesser Sciatic Notch Pain
Lesser sciatic notch pain is relatively uncommon and usually indicates an issue with the structures passing through or near the notch rather than the bone itself. Conditions like piriformis syndrome or nerve impingement could cause pain in this region. These conditions often affect the obturator internus muscle or nearby nerves that traverse the lesser sciatic notch. To diagnose the root cause of the pain, doctors usually perform physical examinations, imaging tests, and sometimes nerve conduction studies. Treatment may include physical therapy, medication for pain relief, or surgical intervention in severe cases.
What Structure Passes Through The Lesser Sciatic Notch?
The obturator internus muscle passes through the lesser sciatic notch as it exits the pelvis to attach to the femur. This muscle plays a role in rotating the hip and stabilizing the hip joint. Additionally, specific nerves and vessels also traverse this notch. The lesser sciatic notch is a critical anatomical gateway, allowing these structures to move between the pelvic cavity and the posterior thigh. It essentially acts as a conduit for both muscular and neurovascular elements essential for lower extremity function.
The Relationship Between The Lesser Sciatic Notch And Sciatica
Anatomy plays a significant role in the development and management of sciatica. Let’s explore how it can impact the sciatic nerve and contribute to sciatica symptoms.
Anatomy Of The Lesser Sciatic Notch
The lesser sciatic notch is a small opening in the ischium bone. It provides a passageway for several important structures, including the sciatic nerve, blood vessels, and tendons. When it becomes constricted or impinged, it can pressure the sciatic nerve, leading to sciatica symptoms.
What Forms The Sciatic Notch?
The sciatic notch forms in the pelvic bone, specifically in the ilium. The greater sciatic notch lies above the ischial spine, and the lesser sciatic notch sits below it. Both notches serve as anatomical pathways for various structures. The sacrospinous and sacrotuberous ligaments convert these notches into foramina, creating tunnels for nerves and muscles. These notches play crucial roles in skeletal anatomy and facilitate the passage of important soft tissue structures like the sciatic nerve and obturator internus muscle.
How The Lesser Sciatic Notch Can Affect The Sciatic Nerve
A narrowed or inflamed lesser sciatic notch can compress the sciatic nerve, causing it to become irritated or pinched. This compression can result in the characteristic pain, numbness, and tingling sensations associated with sciatica. Understanding this relationship emphasizes the importance of caring, alleviating symptoms, and preventing future occurrences.
Sciatic Notch Pain Treatment
Doctors usually conduct a thorough diagnosis involving physical examinations and imaging tests such as MRIs or X-rays to treat pain in the sciatic notch region. Treatment options vary once they identify the root cause, often related to conditions like sciatica or piriformis syndrome. Physical therapy exercises stretch and strengthen affected muscles, improving mobility and reducing pain. Anti-inflammatory medications or muscle relaxants can alleviate pain and inflammation. Corticosteroid injections offer temporary relief from nerve irritation. In severe or persistent cases, surgical intervention, such as decompression surgery, may be necessary to relieve pressure on the affected nerves. Treatment choice typically depends on the underlying cause and severity of symptoms.
Managing Sciatica Through Lesser Sciatic Notch Care
To effectively manage sciatica, addressing the health of the lesser sciatic notch is crucial. Here are some practical strategies to consider:
Stretching And Strengthening Exercises
Engaging in regular stretching and strengthening exercises can help improve the flexibility and strength of the muscles surrounding the lesser sciatic notch. Focus on exercises that target the hip, gluteal, and pelvic areas, as these can alleviate pressure on the sciatic nerve.
Posture And Ergonomics
Maintaining proper posture and ergonomics is essential for reducing strain on the lesser sciatic notch and preventing sciatica. Pay attention to your sitting and standing posture, ensuring that your spine is properly aligned and well-supported. Invest in ergonomic furniture or utilize cushions and lumbar support when necessary.
Pain Management Techniques
Incorporating pain management techniques can provide relief during episodes of sciatica. Consider applying hot or cold packs to the affected area, practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing and meditation, or using over-the-counter pain medications as directed by a healthcare professional.
Preventing Sciatica By Caring For The Lesser Sciatic Notch
Taking proactive steps to care for the lesser sciatic notch can significantly reduce the risk of developing sciatica. Consider the following suggestions:
Importance Of Maintaining Health
By prioritizing the health of the lesser sciatic notch, you can minimize the likelihood of compression or impingement on the sciatic nerve. A healthy lesser sciatic notch allows for smooth passage of the sciatic nerve and other structures, reducing the chances of sciatica.
Lifestyle Modifications
Incorporate healthy habits into your daily routine to promote lesser sciatic-notch health. This includes maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, avoiding prolonged periods of sitting or standing, and practicing good posture and body mechanics during activities.
Seeking Professional Help For Sciatica Issues

While self-care strategies can be effective, seeking professional help when dealing with sciatica issues is essential. Consulting a healthcare provider can provide tailored guidance and treatment options based on your specific condition. Consider the following:
When To Consult A Healthcare Provider
If your sciatica symptoms persist or worsen despite self-care efforts, or if you experience severe or debilitating pain, it is crucial to seek medical attention. Additionally, if you notice any changes in bowel or bladder function along with sciatica, it is important to consult a healthcare professional promptly.
Treatment Options And Therapies
Healthcare providers may recommend a variety of treatment options for sciatica issues. These may include physical therapy, chiropractic care, pain medication, injections, or in severe cases, surgical intervention. Your healthcare provider will evaluate your condition and determine the most appropriate course of action.
Conclusion
Understanding the impact of the lesser sciatic notch on sciatica can provide valuable insights into managing and preventing this condition. By caring for the health of the lesser sciatic notch through exercises, posture correction, and lifestyle modifications, you can alleviate symptoms and promote overall well-being. Remember, seeking professional help when necessary ensure that you receive personalized guidance and appropriate treatment options.
Please note that this article should not replace professional medical advice. Consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plan.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can sciatica be cured completely?
Sciatica can often be effectively managed, and symptoms can be alleviated. However, the underlying causes may still require ongoing management.
How long does it take to recover from sciatica?
The recovery time for sciatica can vary depending on the individual and the severity of the condition. It can range from a few weeks to several months.
Can poor posture contribute to sciatica?
Yes, poor posture can contribute to sciatica. Slouching or sitting in positions that strain the spine and compress the sciatic nerve can increase the risk of developing or worsening sciatica.
What is the sciatic notch and how does it determine gender?
The sciatic notch is a curve in the pelvic bone that serves as a passageway for nerves and muscles. Its shape can help determine gender in skeletal remains; a wider angle often suggests a female pelvis, while a narrower angle indicates a male.
Can stress worsen sciatica symptoms?
Stress can contribute to muscle tension and inflammation, which may exacerbate sciatica symptoms. Implementing stress-reducing techniques such as massage, meditation, or relaxation exercises can be beneficial in managing sciatica.
Extra FAQs Related To Lesser Sciatic Notch
What converts sciatic notch to foramen?
The sacrospinous and sacrotuberous ligaments convert the greater and lesser sciatic notches into foramina. These ligaments attach to the pelvic bone, creating tunnels that allow the passage of nerves and muscles between the pelvis and lower extremities.
Are there any natural remedies for sciatica pain?
Some natural remedies that may help alleviate sciatica pain include applying hot or cold packs, practicing yoga or gentle stretching exercises, and using herbal remedies with anti-inflammatory properties. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before trying any natural remedies.
What causes pain in the sciatic notch?
Pain in the sciatic notch often stems from conditions like sciatica or piriformis syndrome, which affect nerves and muscles passing through the area. Inflammation, nerve compression, or muscle spasms can irritate these structures, leading to pain in the sciatic notch region.